In unraveling the multifaceted nature of society, we embark on a journey that extends beyond the simplicity of a dictionary definition. While Oxford Languages may characterize society as the aggregate of people in an ordered community, a closer examination reveals an infinitely complex network of individuals. This exploration delves into the global interconnectedness of social groups on our modest planet and the subtle intricacies embedded in individual behaviors.
Consider the binary nature of many decisions that individuals face daily – a constant contemplation of what one should or shouldn’t do. This internal dialogue is heavily influenced by societal norms, the unwritten rules that dictate what is deemed right or wrong. These norms, in turn, mold our interactions, manifesting in subtle aspects like posture and tone during conversations or more overt gestures, such as holding a door open for someone. The common thread tying these diverse elements together is the pervasive influence of society on our lives.
Venturing into the academic realms of Sociology and Anthropology, we encounter disciplines dedicated to unraveling the complexities of human existence from its origins to the present day. Among the intellectual giants who have significantly shaped our understanding of society, four figures stand out:
Auguste Comte, known as the father of Sociology, emphasized the importance of scientific methods in comprehending societal dynamics through his advocacy of Positivism. Broken down into three stages, positivism asserts that scientific proof (positive stage) is the only valid conclusion. Metaphysics and theism are rejected.
Herbert Spencer’s contributions, rooted in social Darwinism, introduced the concept of the survival of the fittest in societal evolution. Under this premise, societies are subject to the same laws of natural selection, coined by Charles Darwin.
How many societies before us have failed?
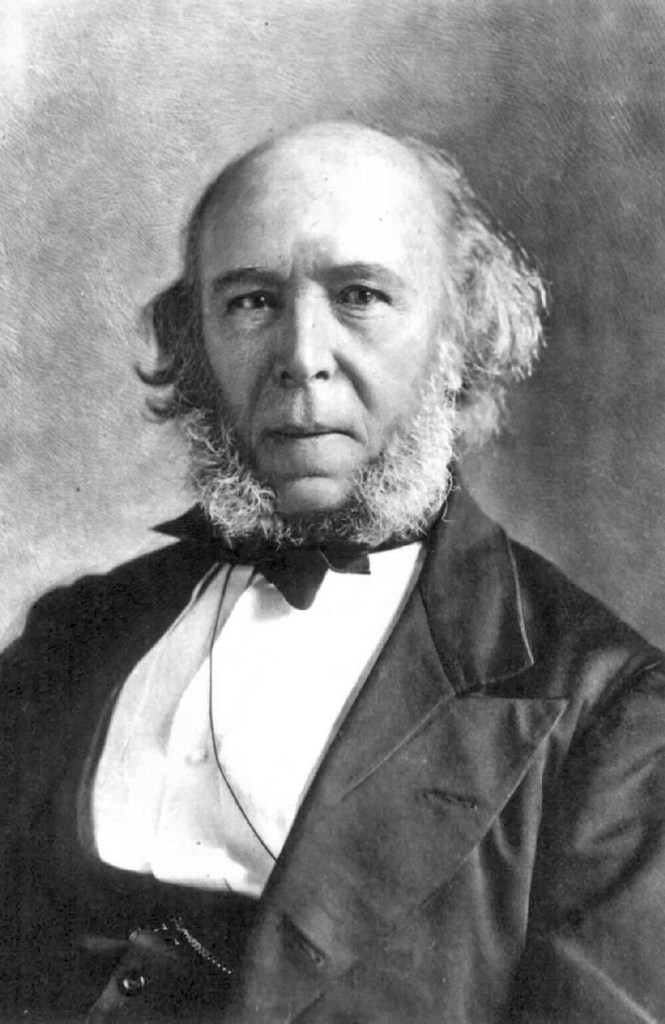

Karl Marx’s enduring ideas on class struggle and capitalism remain influential, offering critical perspectives on economic structures and power dynamics. Utopian Socialism was Marx’s vision of the ideal society. Marxism states the belief that capitalism is a flawed system and is destined for failure for several reasons including the economic strain is too severe on the lower class, the bourgeoisie alienate the proletariat potentially causing revolution and distribution of wealth and privileges are uneven.
How has his theory aged over time?

Emile Durkheim, meanwhile, explored the significance of social integration and collective consciousness in shaping societal cohesion. He believed that society has a powerful (positive or negative) influence on individuals. Anomie, a condition named by Durkheim, is the lack of social or ethical standards in an individual or group. He connected high suicide rates to anomie through his studies.
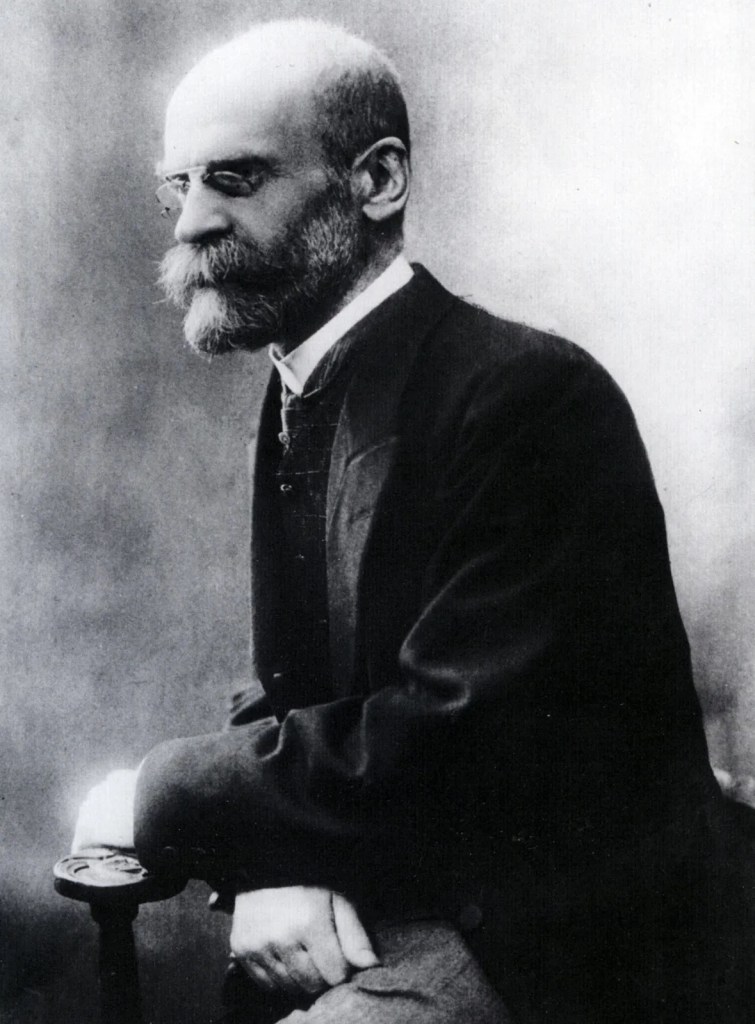

These intellectual luminaries represent just a fraction of the myriad voices that have contributed to the intricate puzzle of society. To truly comprehend the multifaceted nature of society and effectively address its challenges, we must embrace a continuous exploration that surpasses mere definitions. This entails digging deep into the intricacies of societal norms, cultural dynamics, and historical influences that shape our collective existence.
In this expanding landscape, each experience from individuals and communities contributes to the rich nature of human life. By acknowledging the diverse perspectives within society, we gain a more comprehensive understanding of the forces that drive individual behaviors and shape the overarching structures of our shared existence. Thus, the exploration of society becomes an ongoing dialogue, a journey that extends beyond the confines of academic disciplines and dictionary entries, inviting us to unravel its intricacies.


Leave a comment