Human societies, with their intricate customs, shared norms, and collaborative structures, have a rich tapestry woven through the fabric of time. Understanding the roots of these societies unveils a fascinating journey from our early ancestors to the complex civilizations we navigate today.
The Dawn of Society
Our journey commences in the distant past, a time when early humans recognized the advantages of cooperation. Survival was number 1 on the (very short) mental list of priorities. Living in groups provided protection, shared resources, and a network of support for survival [Source: Diamond, J. (1997). “Guns, Germs, and Steel”].
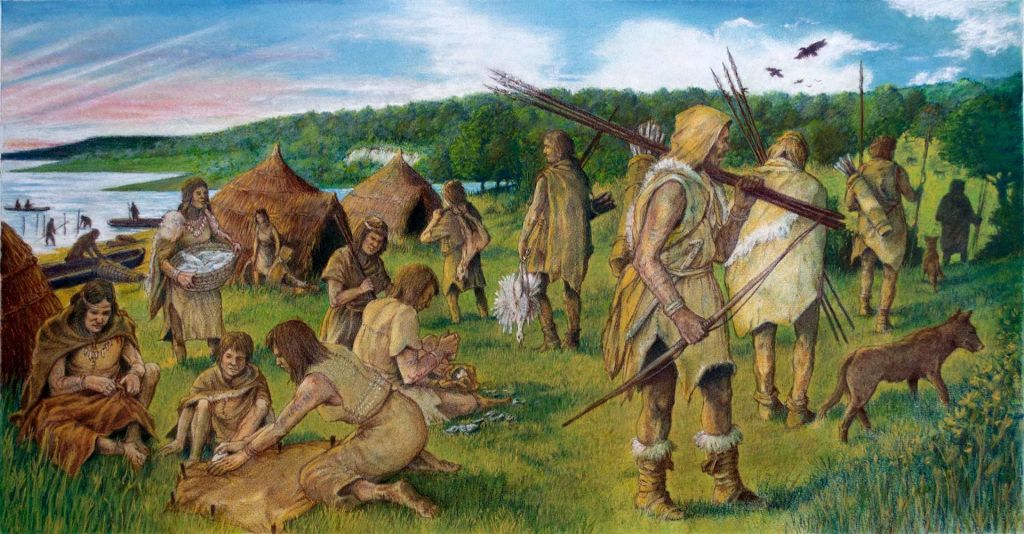
Hunter-Gatherer Communities
The earliest human societies emerged as small, nomadic groups of hunter-gatherers. Their survival depended on the skills and knowledge of each member, fostering a lifestyle of cooperation and communication [Source: Harari, Y. N. (2014). “Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind”].

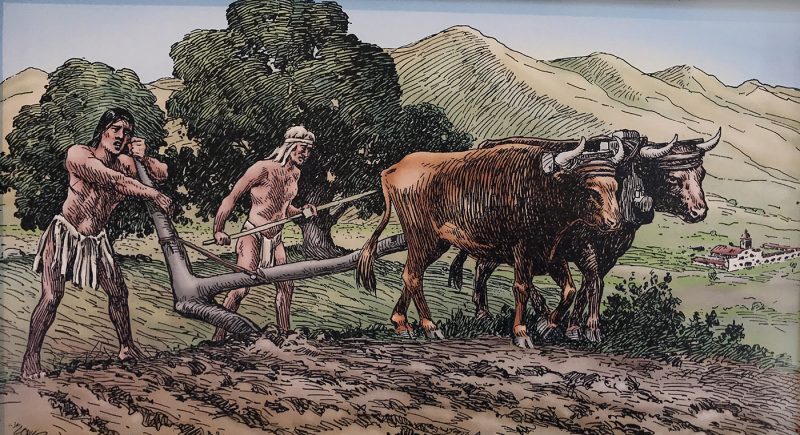
Agriculture and Settlements
Around 10,000 years ago, the advent of agriculture marked a pivotal shift. Humans transitioned from nomadic lifestyles to settled communities, cultivating crops and raising livestock. This surplus of food led to larger populations and the birth of organized societies [Source: Diamond, J. (1999). “Collapse: How Societies Choose to Fail or Succeed”].

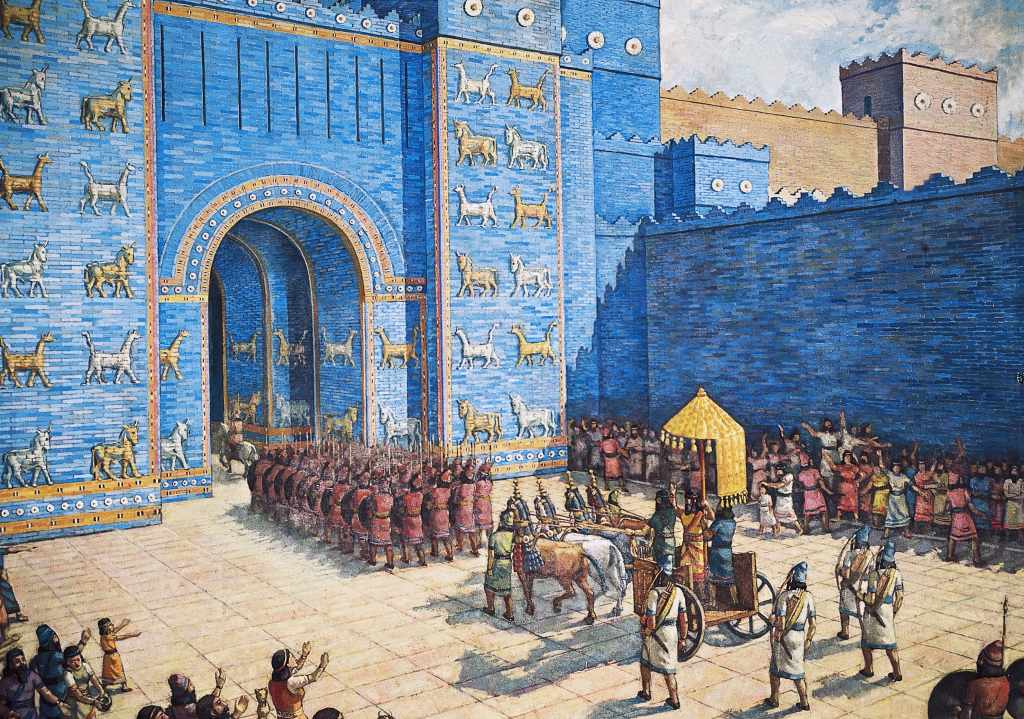
Emergence of Civilizations
Civilizations, marked by complex social structures and advanced technologies, began to flourish around 3,000 BCE. Mesopotamia, Egypt, and the Indus Valley thrived, making monumental advancements in art, science, and governance [Source: Scarre, C. (2005). “The Human Past: World Prehistory and the Development of Human Societies”].

Societal Norms and Laws
As societies grew in complexity, the development of norms and laws became crucial for maintaining order. Rules governing behavior played a pivotal role in regulating relationships and resolving disputes [Source: Hayek, F. A. (1976). “Law, Legislation and Liberty”].
The Modern World
Today’s society stands at the crossroads of technological innovation and globalization. The industrial revolution and the information age have reshaped how we live and interact, connecting people across the globe like never before [Source: Schwab, K. (2017). “The Fourth Industrial Revolution”].
Society’s Purpose
A sense of purpose is not something new to us. The multifaceted purpose of society provides a sense of belonging, security, and support. It fosters economic, cultural, and technological progress, creating a space where individuals can cooperate, share, and thrive collectively [Source: Rousseau, J. J. (1762). “The Social Contract”].
Challenges and Evolution
While society has made remarkable progress, it faces seemingly endless challenges such as inequality, conflict, and environmental concerns. Yet, societies continue to evolve and adapt, addressing these challenges through innovation, activism, and cooperation. However, there will always be the need for change [Source: United Nations Sustainable Development Goals Report].
Conclusion
Exploring the origins of human communities is necessary (and fascinating) for continuing to improve as humans and as societies. From early hunter-gatherer societies to the complexities of modern civilizations, our journey through time sheds light on the forces that have shaped our world. Understanding these origins not only offers insights into our past but also bridges the gap for positive change in the future. At the end of the day, are humans really much different than they were in these early societies?


Leave a comment